ex3.m
Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data
-
Load Training Data
1 | load('ex3data1.mat'); % training data stored in arrays X, y |
-
Visualization
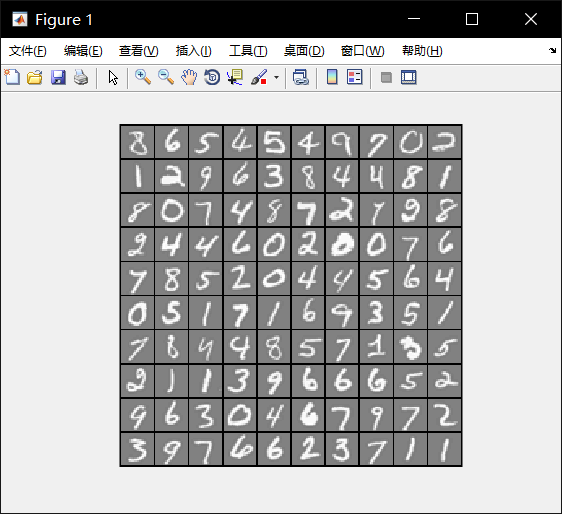
Part 2a: Vectorize Logistic Regression
-
Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta. You should set J to the cost.
Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
1 | J = (1 / m) * sum(-y .* log(sigmoid(X * theta)) - (1 - y) .* log(1 - sigmoid(X * theta))) + (lambda / (2 * m)) * sum(theta(2:size(theta)) .^2); |
Part 2b: One-vs-All Training
-
You should complete the following code to train num_labels logistic regression classifiers with regularization parameter lambda.
1 | % Set Initial theta |
Part 3: Predict for One-Vs-All
-
Complete the following code to make predictions using your learned logistic regression parameters (one-vs-all).
1 | predict = sigmoid(X * all_theta'); |
ex3_nn.m
-
Complete the following code to make predictions using your learned neural network.
1 | X = [ones(m, 1) X]; |
ex4.m
Part 3: Compute Cost (Feedforward)
-
Feedforward the neural network and return the cost in the variable J. After implementing Part 1, you can verify that your cost function computation is correct by verifying the cost computed in ex4.m
1 | % input layer |
Part 4: Implement Regularization
-
You should now add regularization to your cost function. Notice that you can first compute the unregularized cost function J using your existing nnCostFunction.m and then later add the cost for the regularization terms.
1 | % regularized cost function |
Part 5: Sigmoid Gradient
-
Implement the sigmoid gradient function
1 | g = sigmoid(z) .* (1 - sigmoid(z)); |
Part 6: Initializing Pameters
-
Initialize W randomly so that we break the symmetry while training the neural network
1 | % Randomly initialize the weights to small values |
Part 7: Implement Backpropagation
-
Implement the backpropagation algorithm to compute the gradients Theta1_grad and Theta2_grad.
1 | for t = 1:m |
Gradient checking
1 | % take a look and try to understand |
Part 8: Implement Regularization
-
Implement regularization with the cost function and gradients.
1 | Theta1_grad(:, 2:end) = Theta1_grad(:, 2:end) + (lambda / m) * Theta1(:, 2:end); |